Tortrix viridana
Linnaeus, 1758
-
 Subfamily: Tortricinae, Tortricini
Subfamily: Tortricinae, Tortricini -
 Wingspan: 17-24 mm
Wingspan: 17-24 mm -
 Flight period: Apr - Jul
Flight period: Apr - Jul -
 Spread: Common
Spread: Common -
 Host plants: Fagaceae (Polyphagous)
Host plants: Fagaceae (Polyphagous)
Information
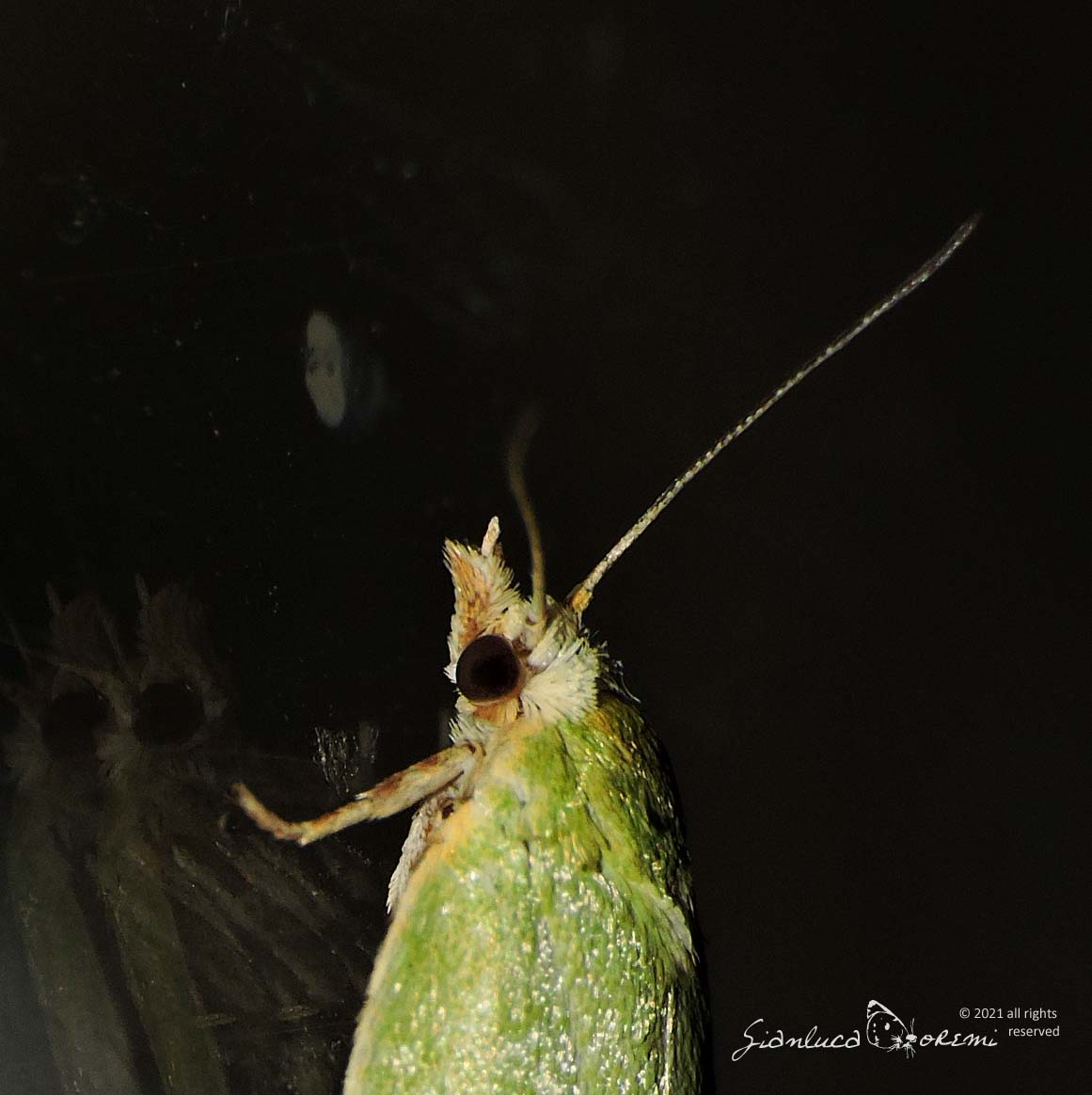
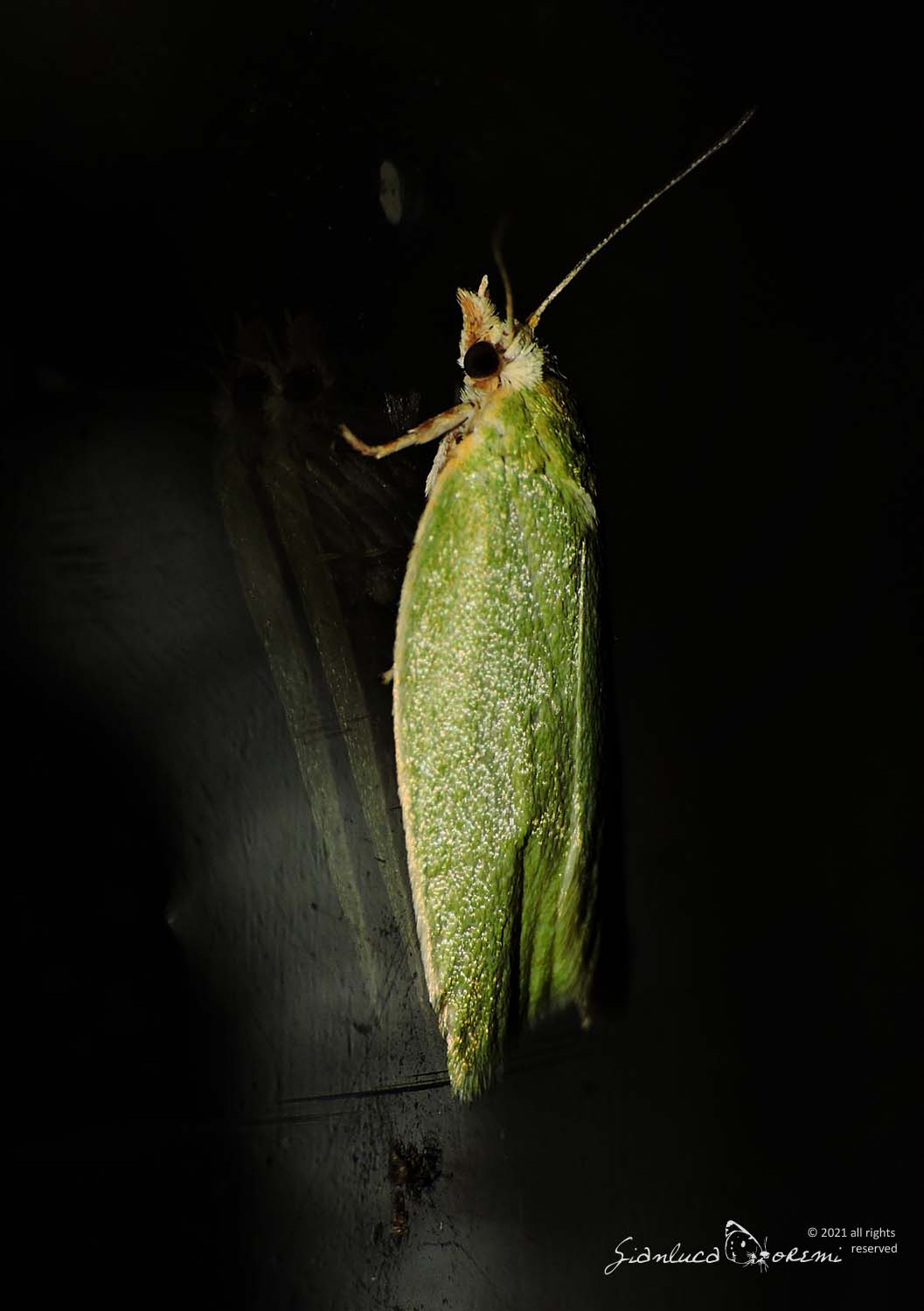
The Tortrix viridana also known as European Oak Leafroller or Green Oak Moth is a moth of the Tortricidae family, subfamily Tortricinae,
with wingspan of about 17-24 mm. Smaller specimens with a wingspan of just 13 mm are known, but such undersized specimens are rare.
Distributed in most of Europe with the exception of Croatia. *
Its range extends to Azerbaijan, Asia Minor and Iran.
In Italy it is also present on the islands. *
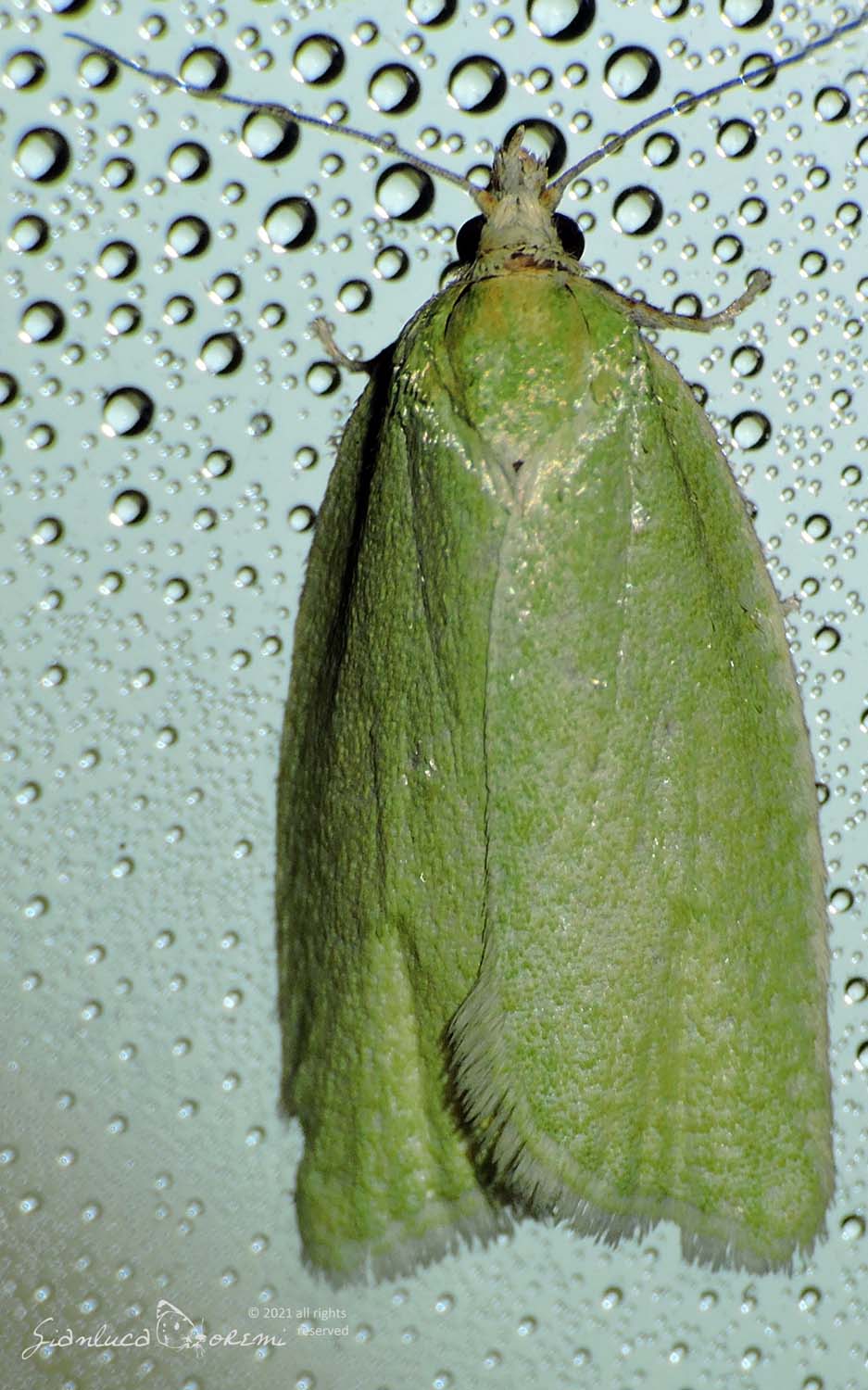
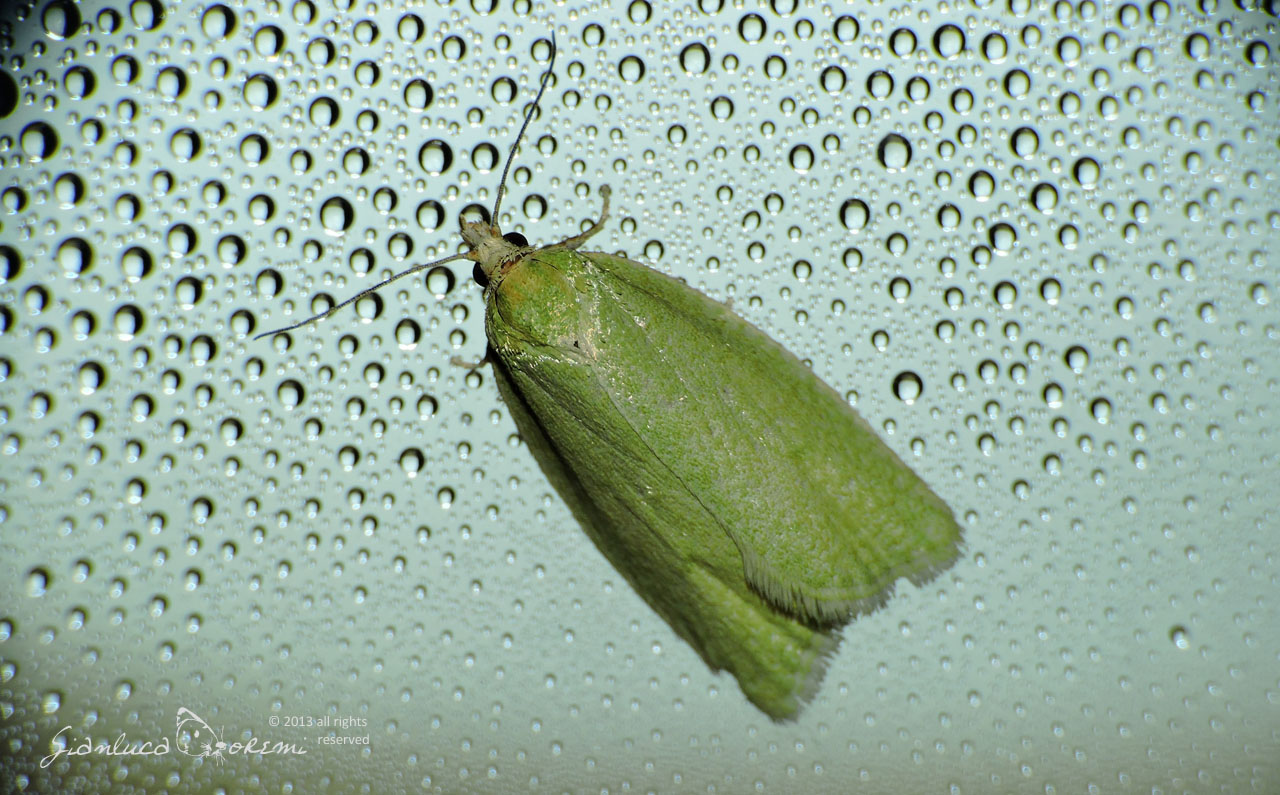
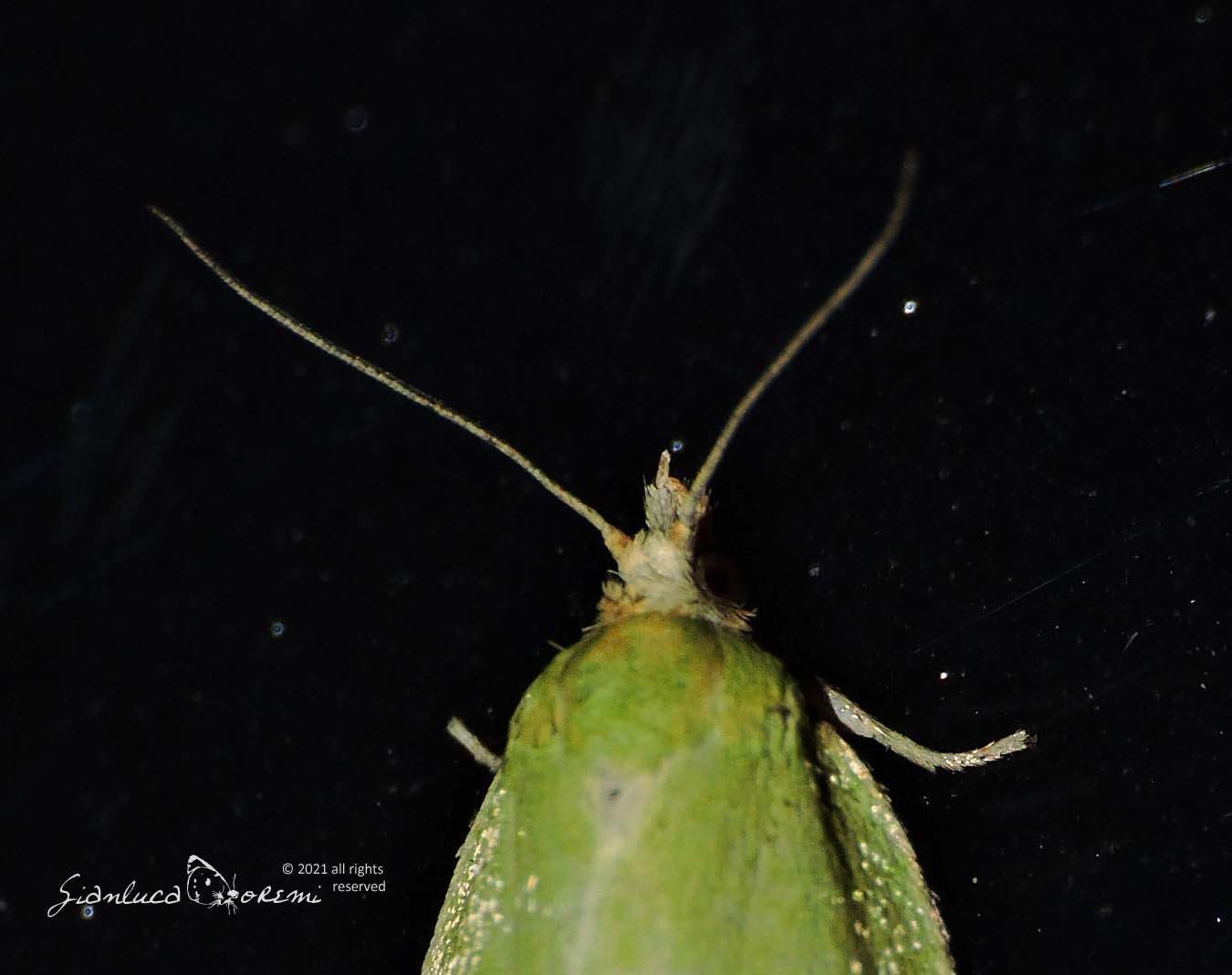
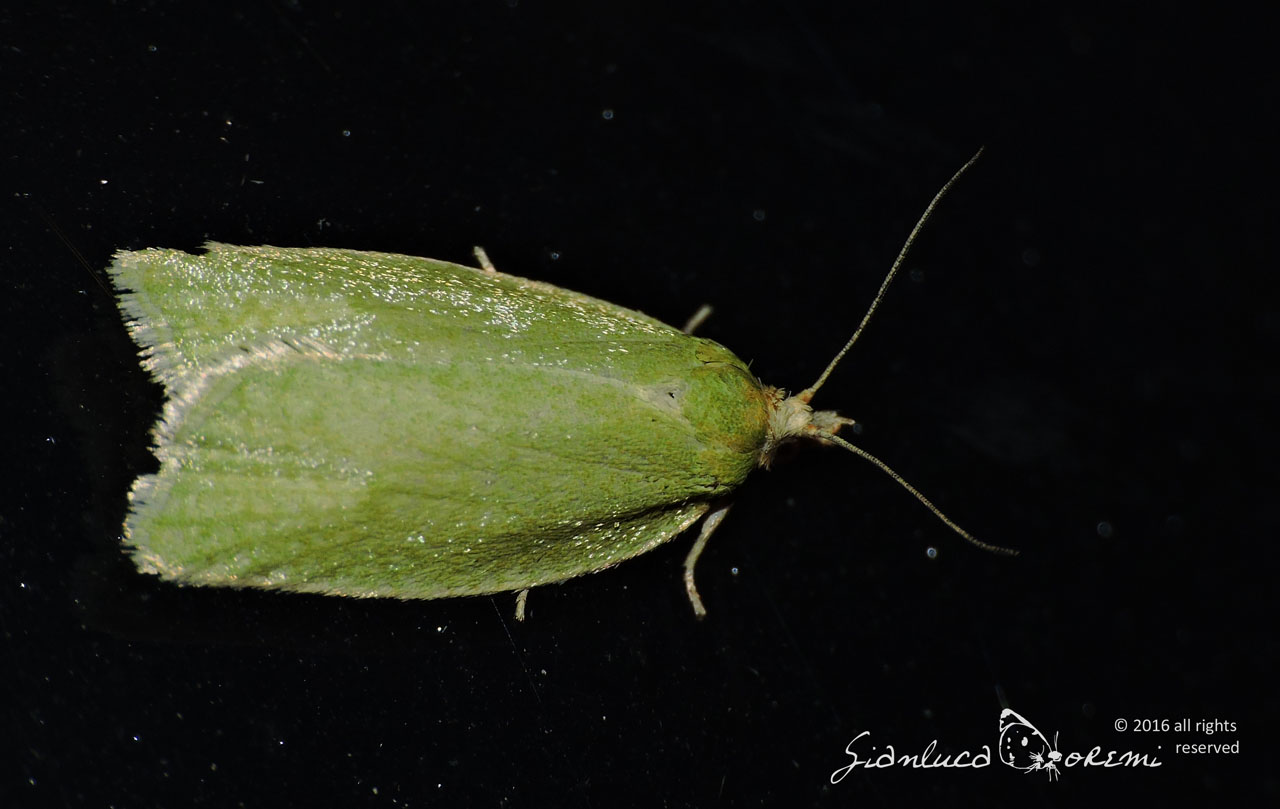
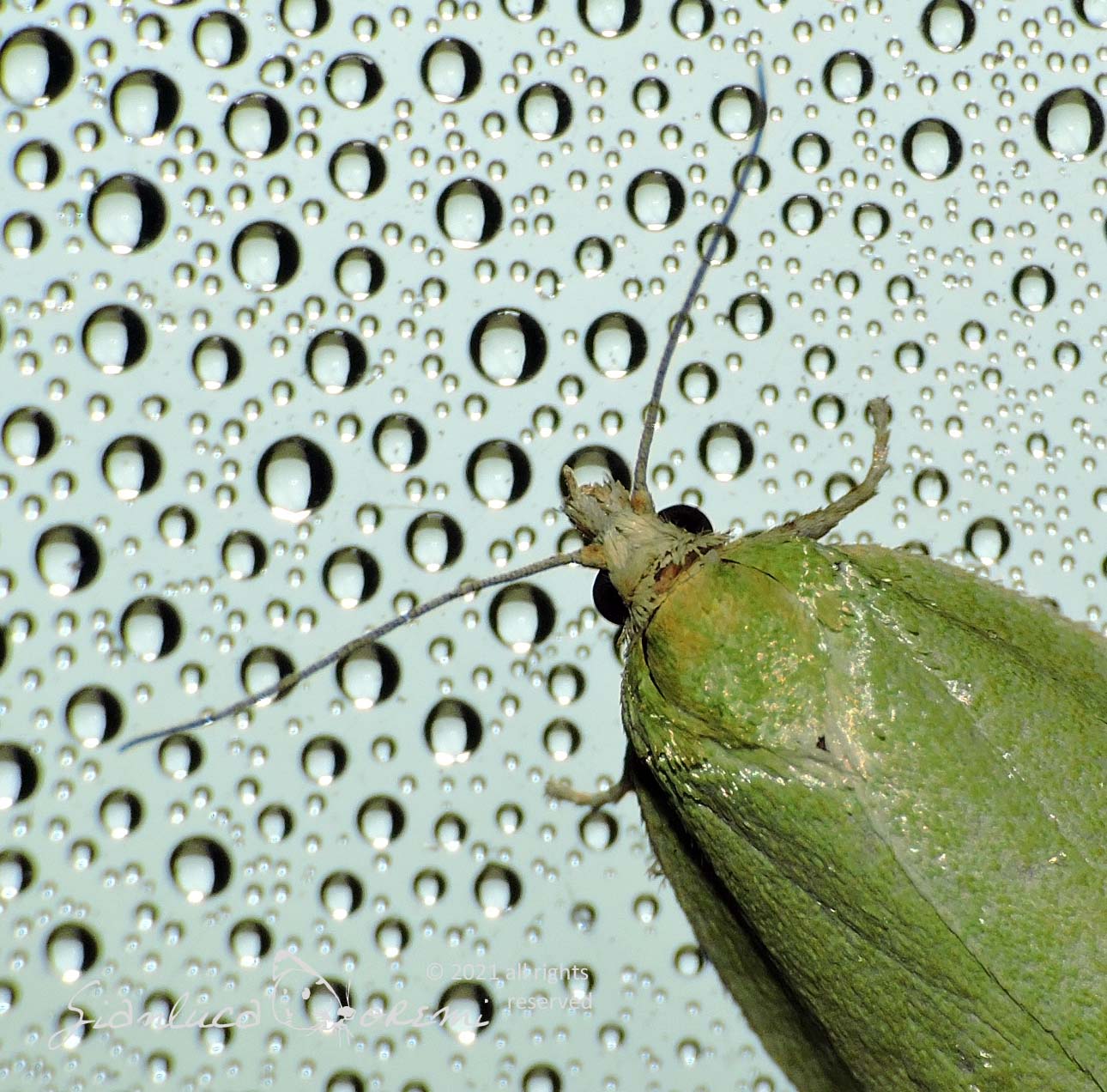
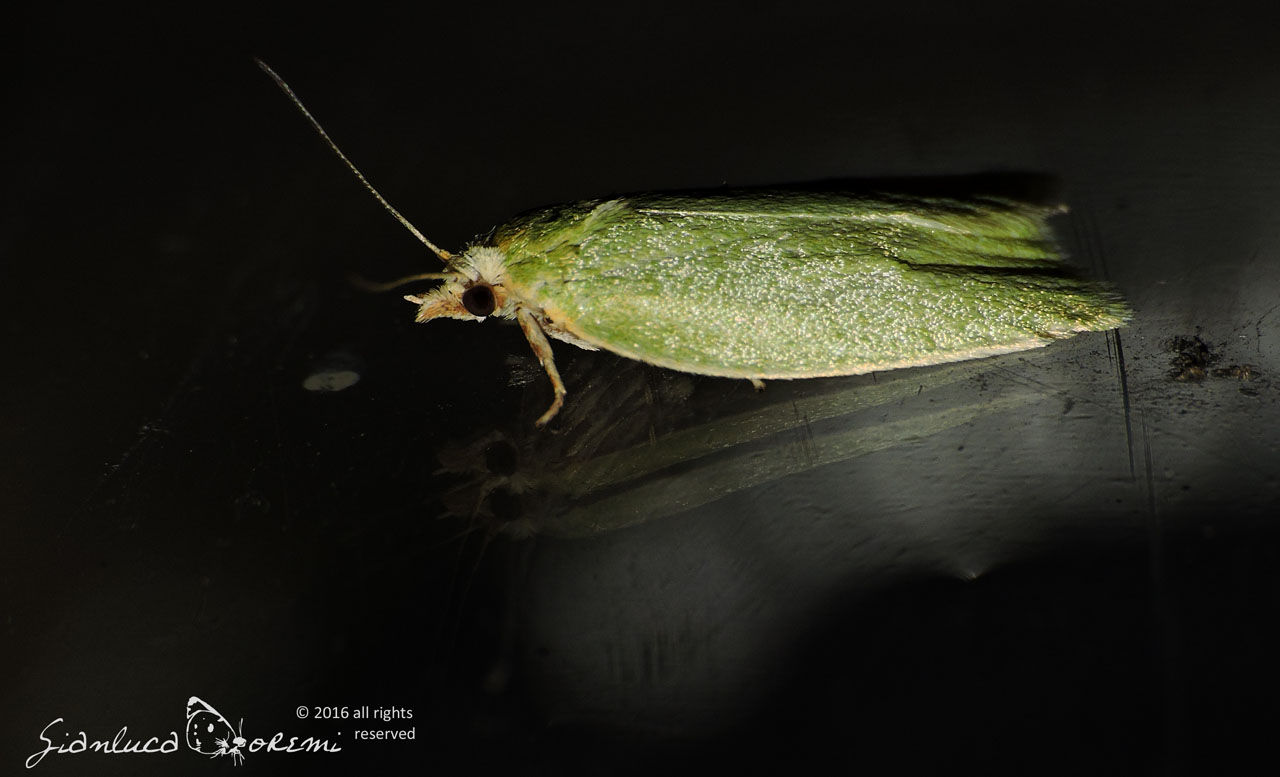
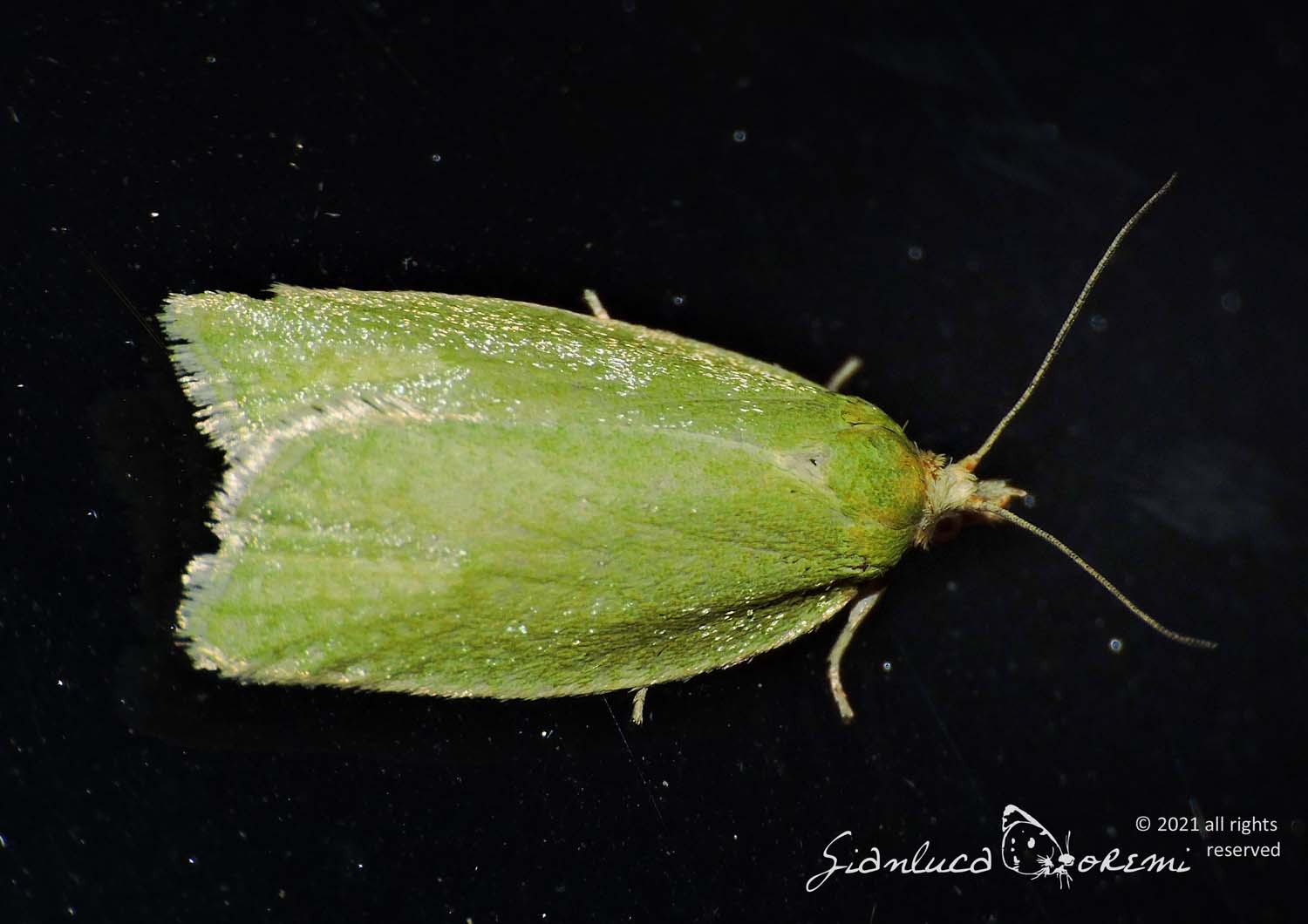
The front wings, the head and the thorax of the Tortrix viridana of a light green color slightly darker in the basal region,
delicate streaks are also visible in the wings.
The costal margin is white tinged with yellow. The marginal area is fringed in white, with a pale green sub-basal line. **, ***
The hind wings are light gray, with a sub-basal gray line around the apex and along the outer edge. **, ***
Sexual dimorphism is not evident. There are specimens in which the green color is replaced by opaque yellow or primrose yellow;
these cases apparently represent a recurrent genetic form and are not due to abrasion or discoloration. ***
Tortrix viridana is a univoltine species with a main flight period from late April / early May (Portugal) to late June / early July (former USSR).
In the UK, adults are more numerous in June and July, and are particularly abundant in oak woodlands.
During the day it settles on the host tree, but is easily disturbed.
The eggs are laid in small batches on the bark, particularly near the leaf bases and where the shoots and small branches divide.
They hatch in the following spring.
The larvae feed from late April to June, initially inside the opening buds, then in rolled or folded leaves.
There are 5 larval stages.
The pupation usually occurs in a leaf folded on the host tree, but the larvae can also descend on a silk thread and pupate on the underlying plants.
When the larvae are present in large numbers, they can defoliate trees before reaching the last larval stage;
under such circumstances the larvae will attack the foliage of various other nearby trees, shrubs and grasses. ****, *****
The eggs are light yellow and then become orange-brown, lenticular in shape, delicately sculpted.
The larva reaches 15-18 mm in length of green-gray or light olive green color, the head is black-brown which tends to black; the prothoracic shield is green-brown or grayish,
marked with blackish-brown, often bordered in front with white and with a pale midline on the thoracic legs black.
The pupa has a length of 10-12 with a color ranging from brown-black to black.
The main host plant is represented by various species of Quercus (oak), but it can also be found on species of Fagus (beech),
Acer (maple), Populus (poplar), Salix (willow), Carpinus (hornbeam), Vaccinium, Urtica (nettle). ******
Older larvae can sometimes complete their development on Rubus idaeus (raspberry). ******
Tortrix viridana is an important parasite of oak, in particular of Quercus robur (English oak).
Although it is mainly a pest in the forest sector, the damage is also caused to trees in parks, gardens and nurseries.
* Lepidoptera mundi https://lepidoptera.eu/ - Fauna Europea https://fauna-eu.org/
** Bestimmungshilfe für die in Europa nachgewiesenen Schmetterlingsarten - http://lepiforum.de/
*** (Bradley et al., 1973)
**** (Alford, 1995)
***** (Bogenschütz, 1991)
****** http://download.ceris.purdue.edu/file/3125










 EN
EN ITA
ITA
Social and publications